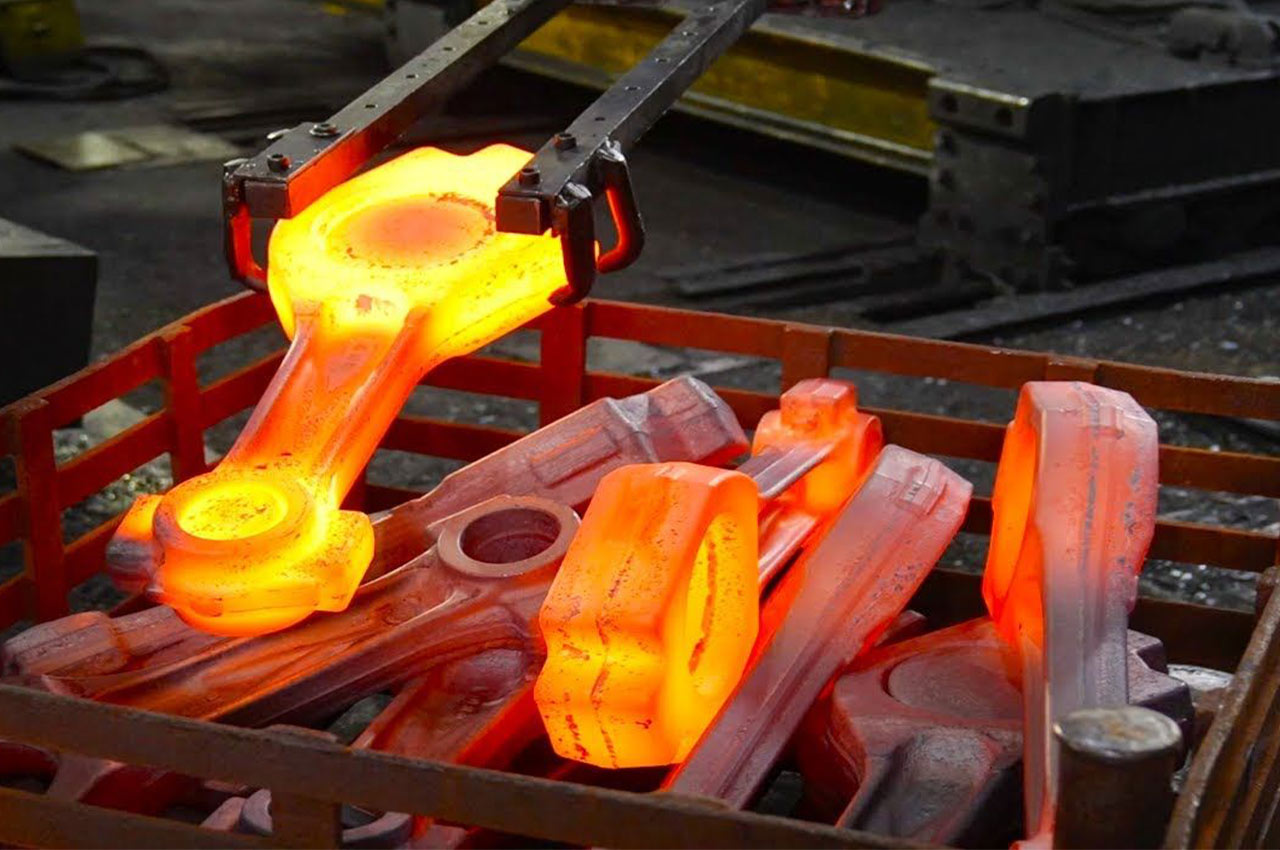
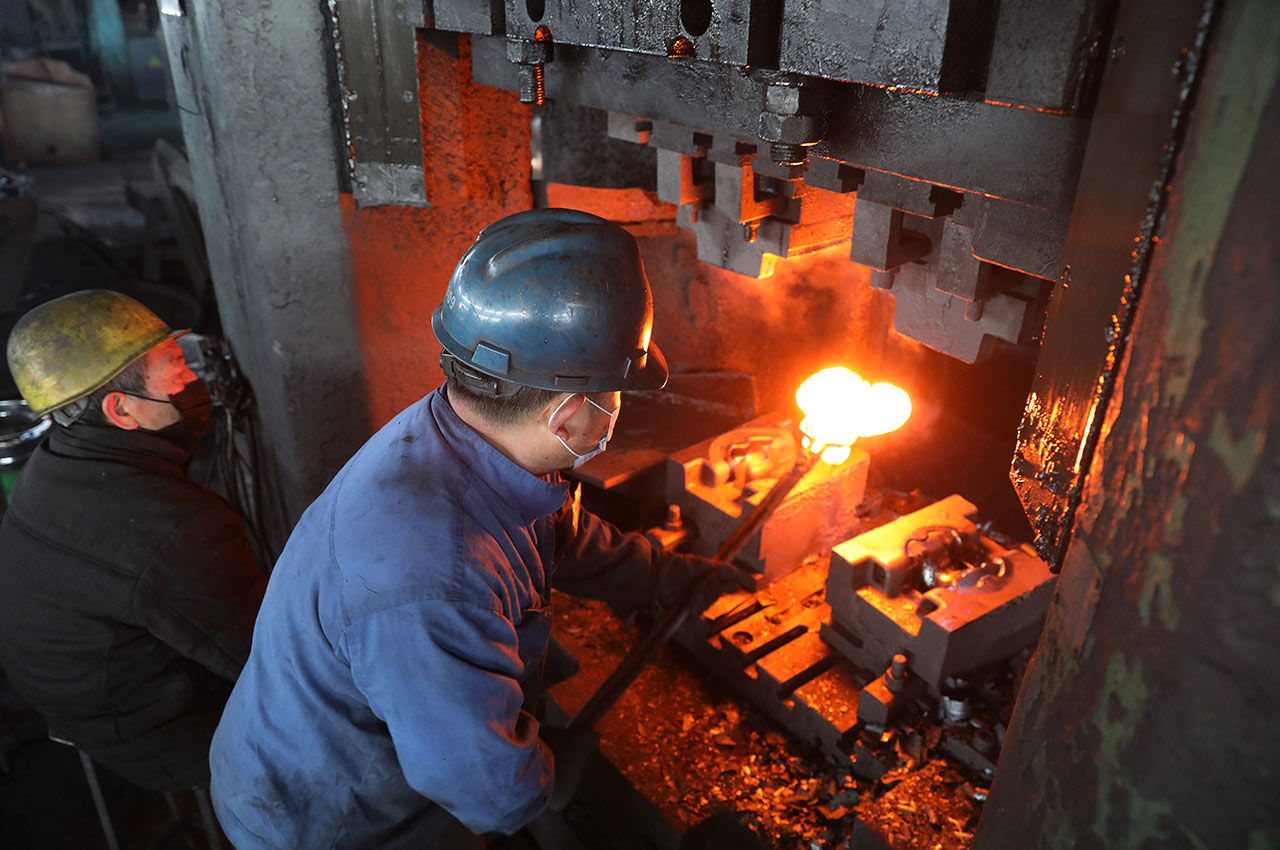
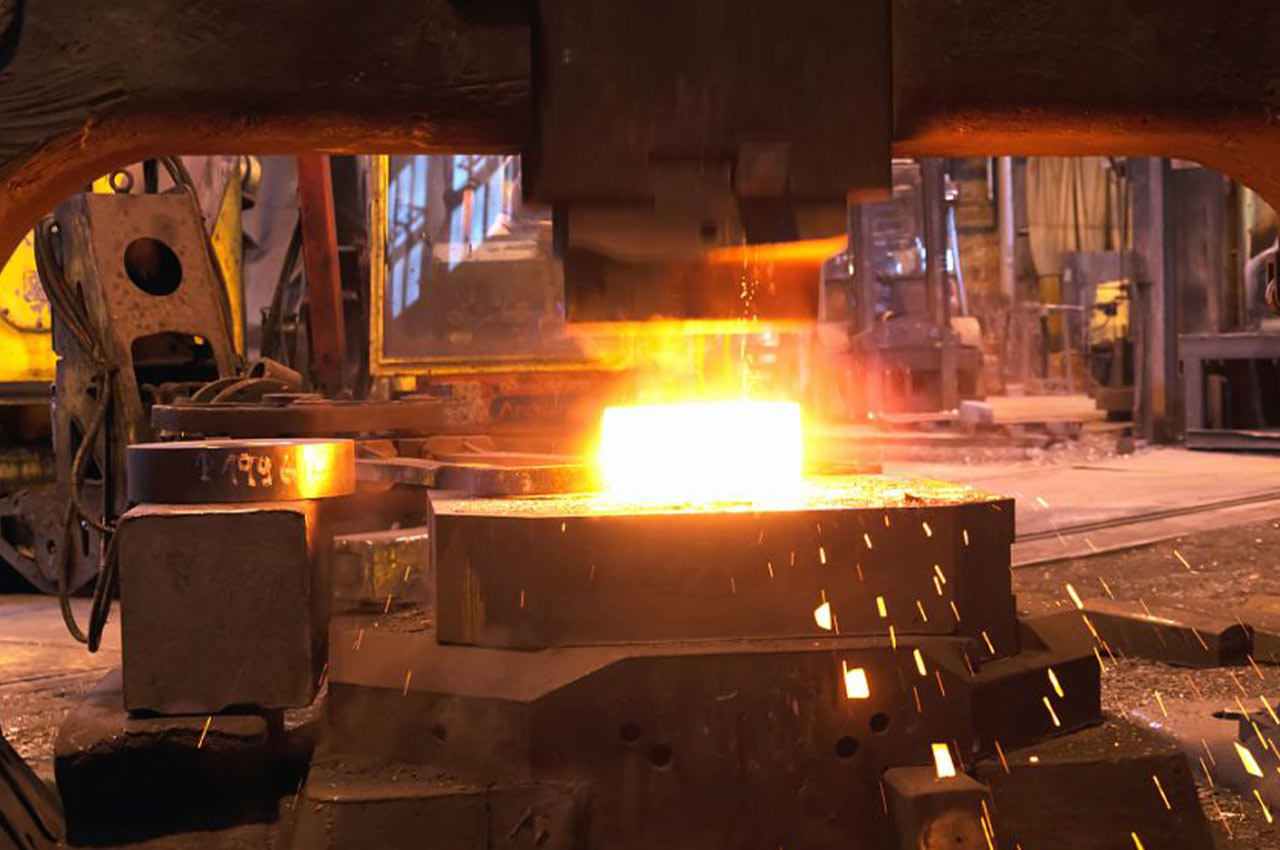
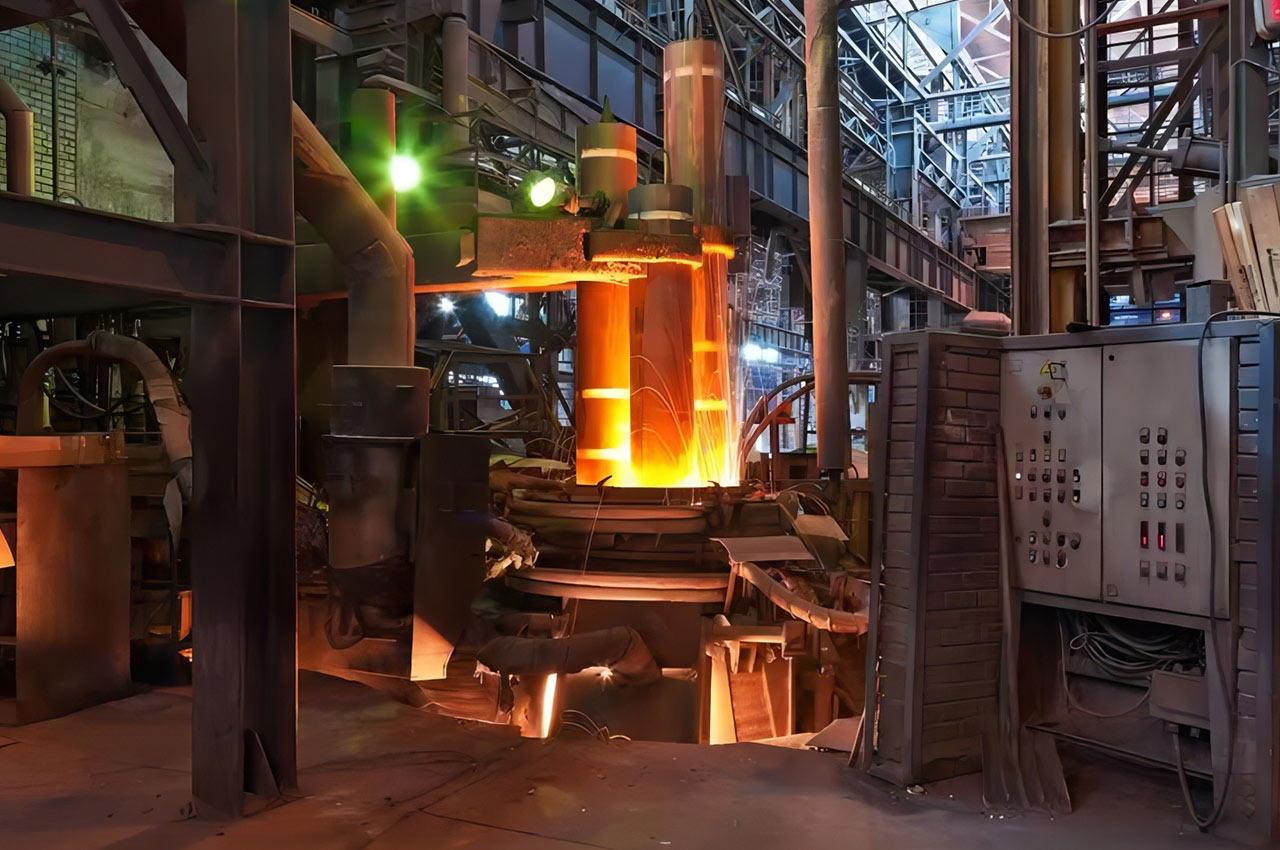
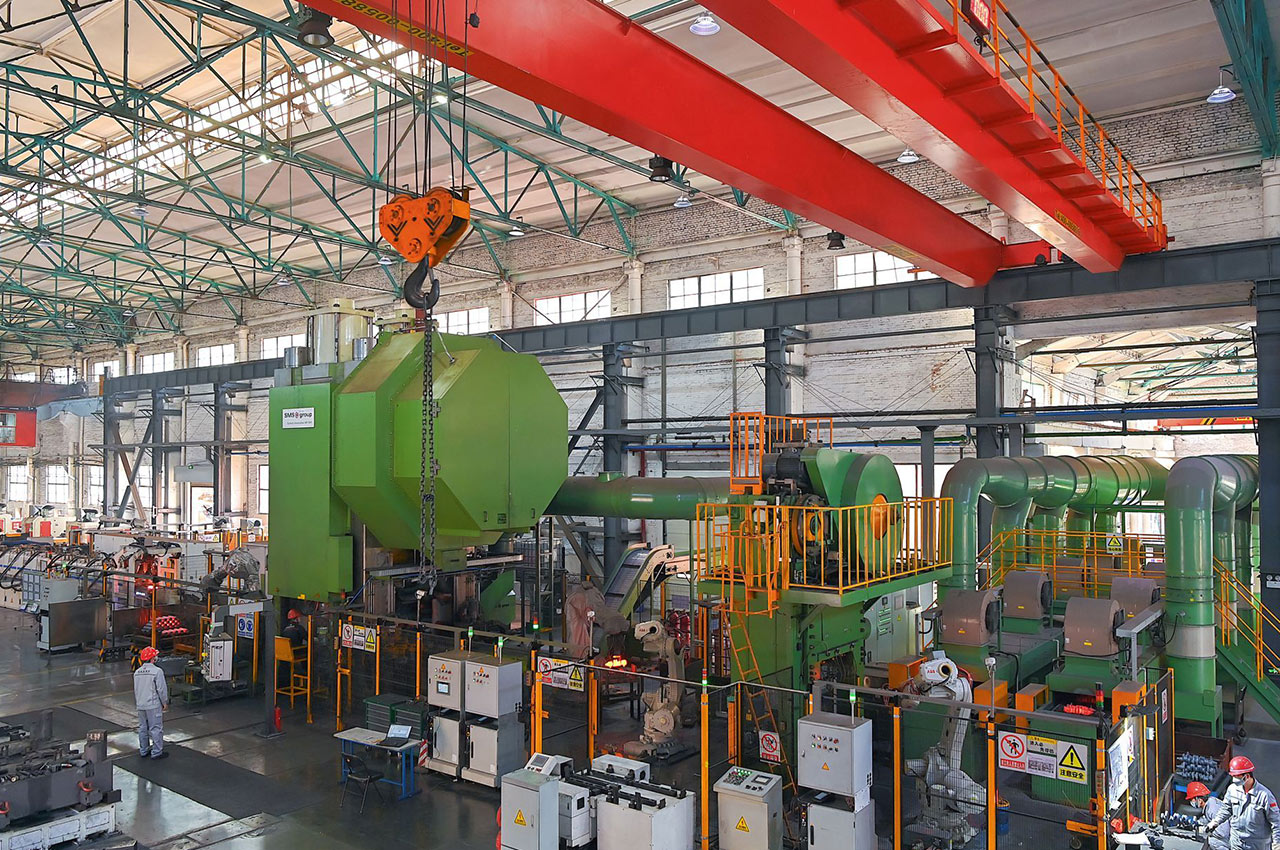
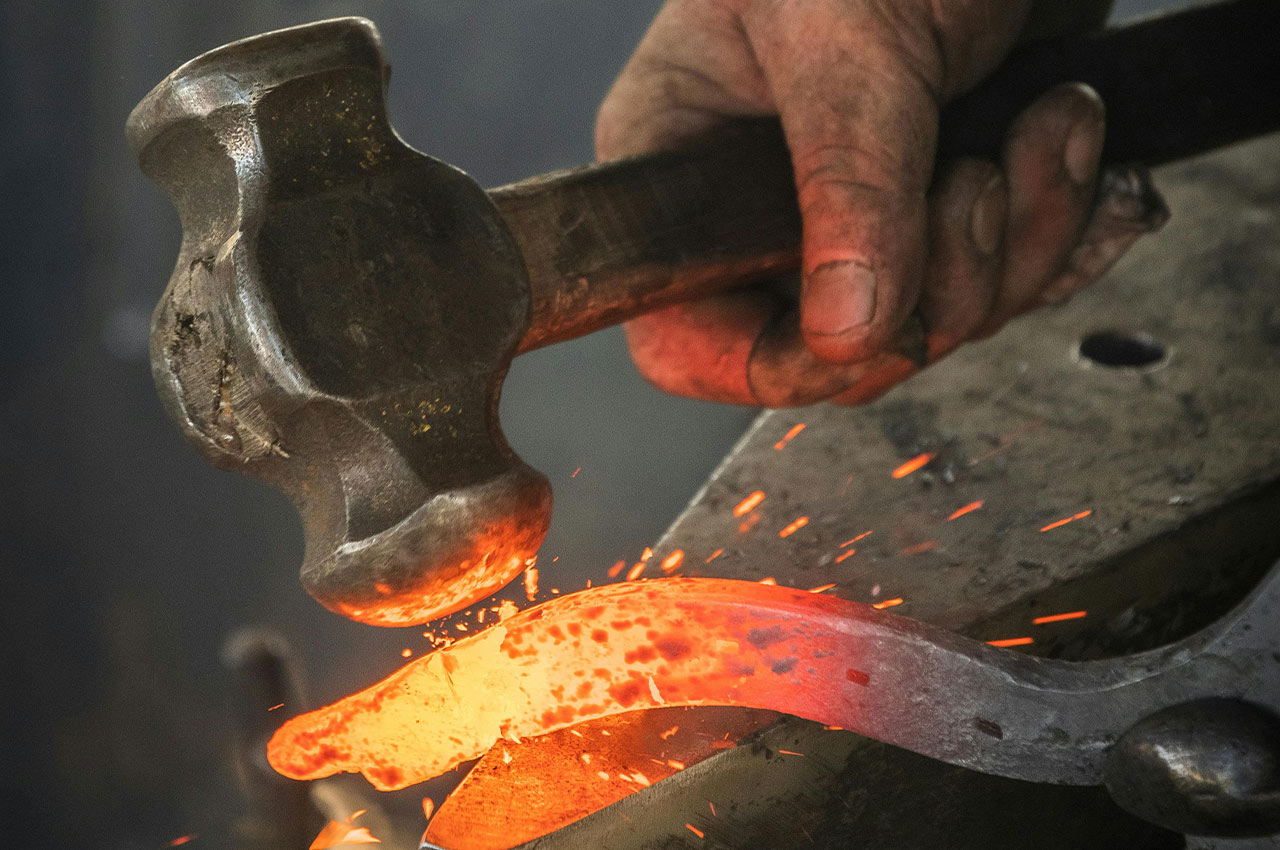
Forging is a metalworking process that causes plastic deformation by applying pressure to metal billets to obtain forgings with a certain shape, size and mechanical properties.


Such as low carbon steel, medium carbon steel and high carbon steel, with good malleability and comprehensive mechanical properties, widely used in the manufacture of all kinds of mechanical parts.

By adding alloying elements (such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, etc.) to improve the performance of steel, it is often used to manufacture parts with high requirements for strength, toughness and wear resistance.
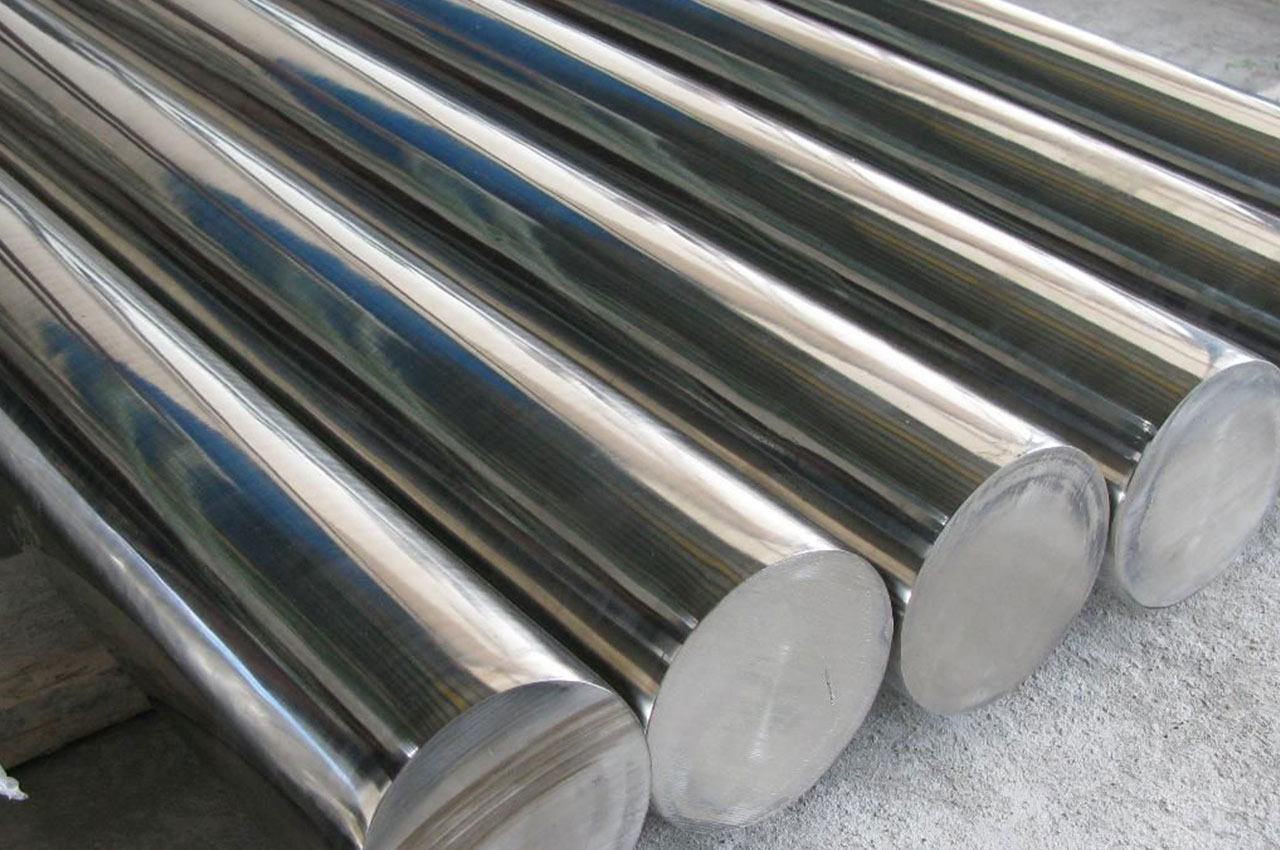

It has good corrosion resistance and is often used to manufacture parts in chemical, medical and other fields.
Such as 2xxx series, 6xxx series and 7xxx series aluminum alloy, with low density, good strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for aerospace, automotive and other fields of lightweight parts.
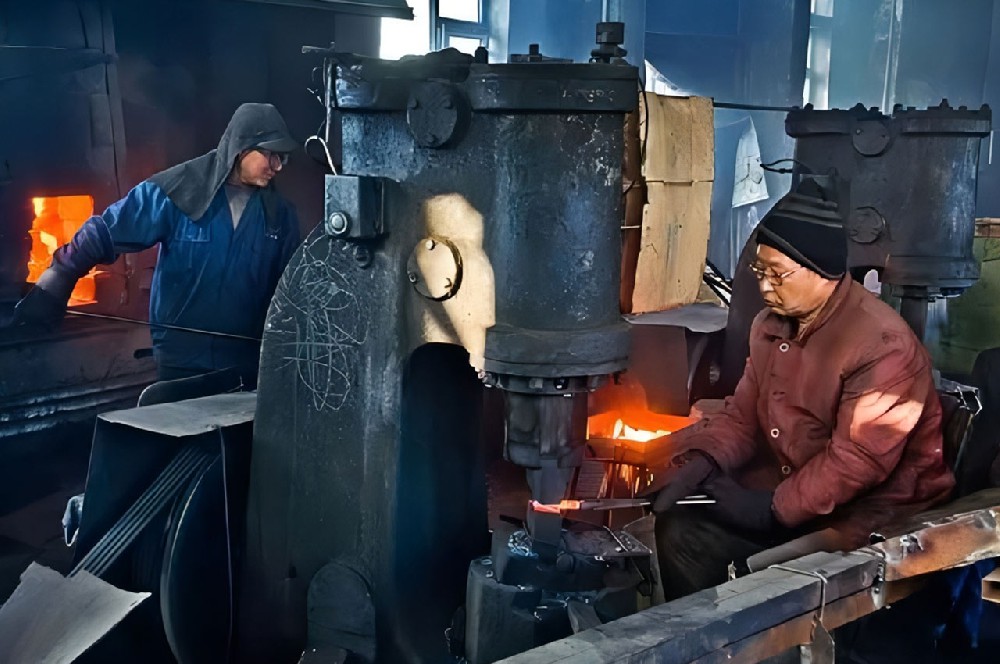

┊ Blanking: Cut or saw off billets of suitable size from raw materials according to the size and weight requirements of the forgings.
┊ Heating: The billet is heated to a specific temperature in a heating furnace to give it good plasticity and facilitate subsequent forging processing.
┊ Forging: A variety of forging methods can be used, such as free forging, die forging, etc.
┊ Trimming: Trimming operations for forgings after forging, such as trimming, punching, and correction, remove excess parts and improve dimensional accuracy and shape accuracy.
┊ Heat treatment: Improve the internal structure and properties of forgings and eliminate forging stress by annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering and other heat treatment processes.
┊ Inspection: Appearance inspection, dimensional measurement, non-destructive testing, etc. of forgings are carried out to ensure that their quality meets the requirements.
┊ Improve the metal structure: through forging can eliminate the metal in the smelting process of as-cast loose and other defects, optimize the microstructure, make the metal flow line complete, improve the mechanical properties of the metal.
┊ Molding accuracy: High dimensional accuracy and surface quality can be obtained.
┊ Strength improvement: the strength, toughness and fatigue strength of metal materials after forging are significantly improved.
┊ Shape limitation: Compared with casting, the molding of complex shape parts is more difficult, and it is more suitable for manufacturing parts with relatively simple and regular shapes.
┊ Mass production: In mass production, it can give full play to its advantages and reduce costs.
┊ Process flexibility: There are a variety of methods such as free forging and model forging, which can be selected according to product needs.




