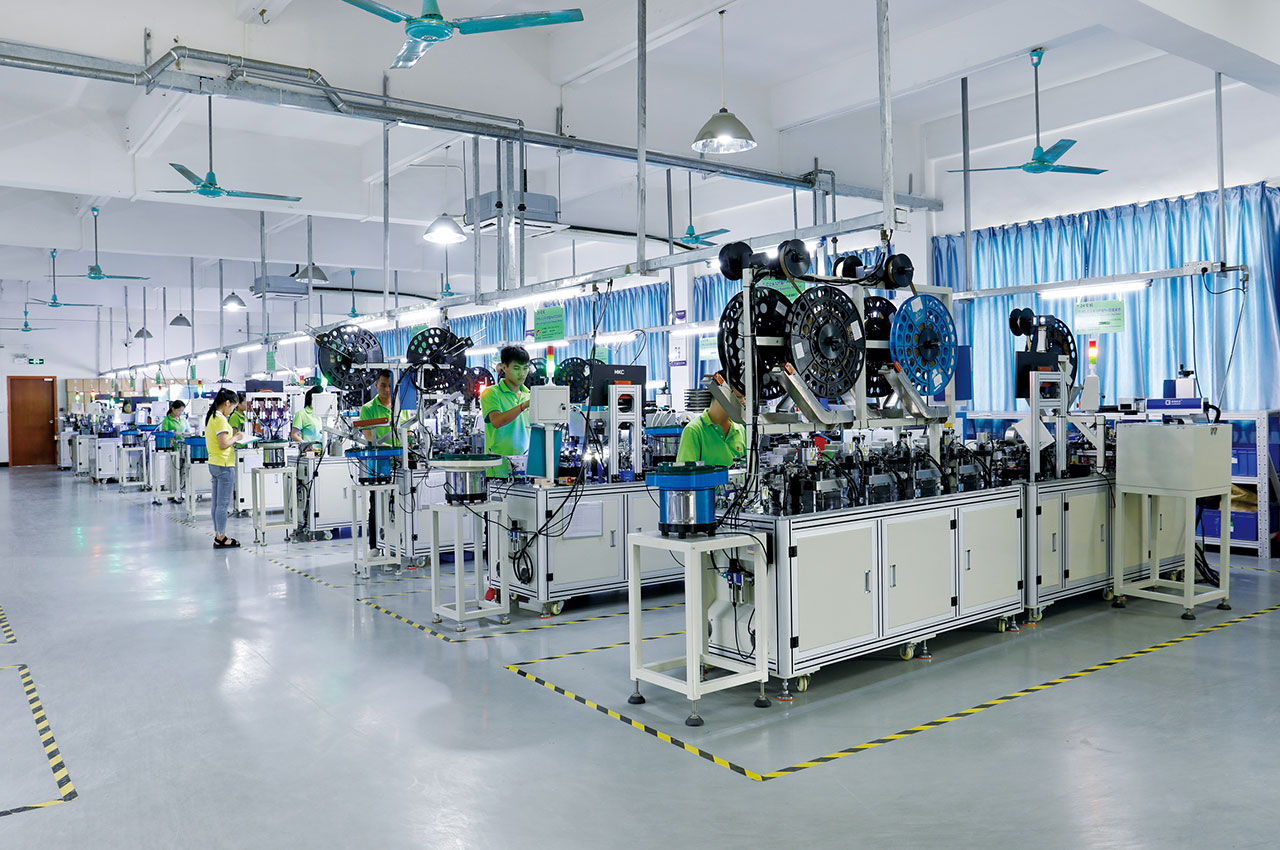
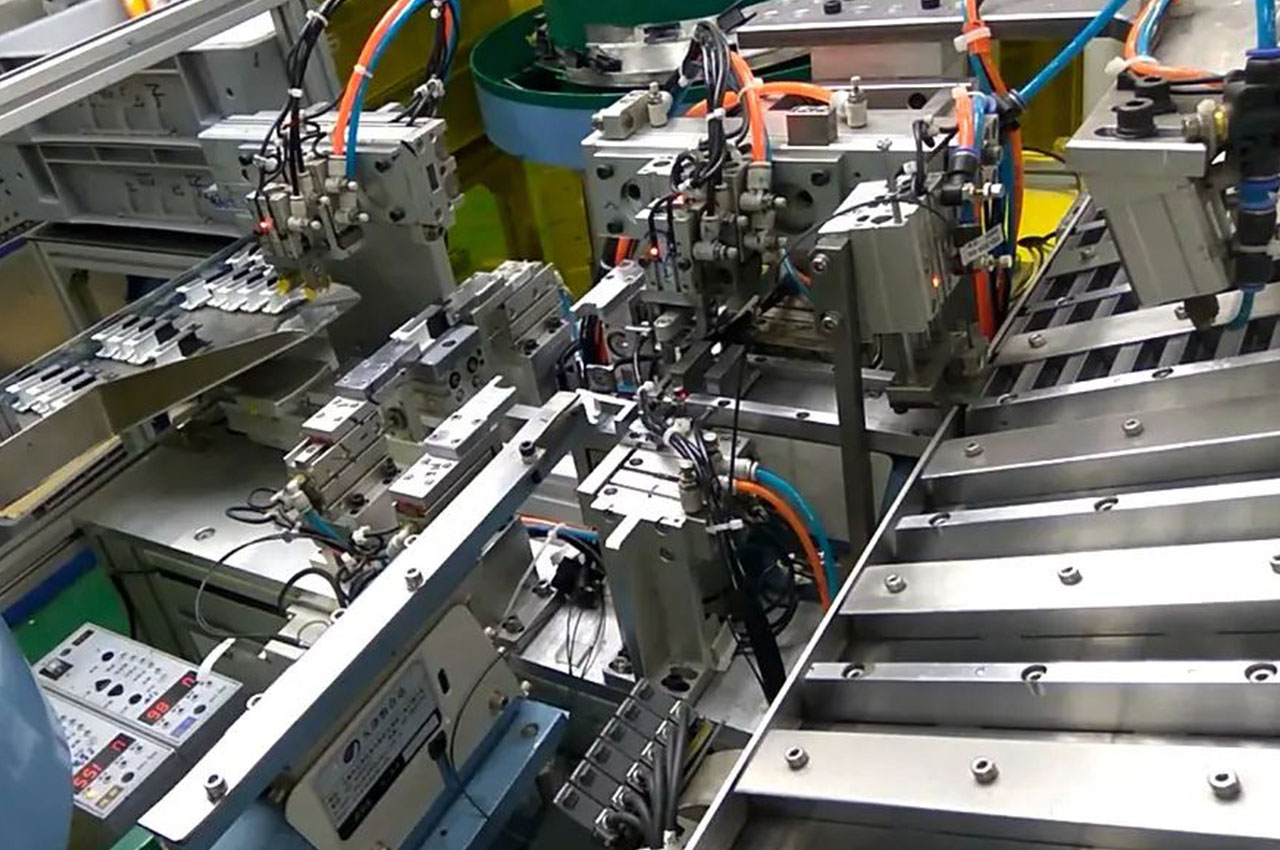
Automated assembly process is the use of automated equipment and technology to complete the process of product assembly.
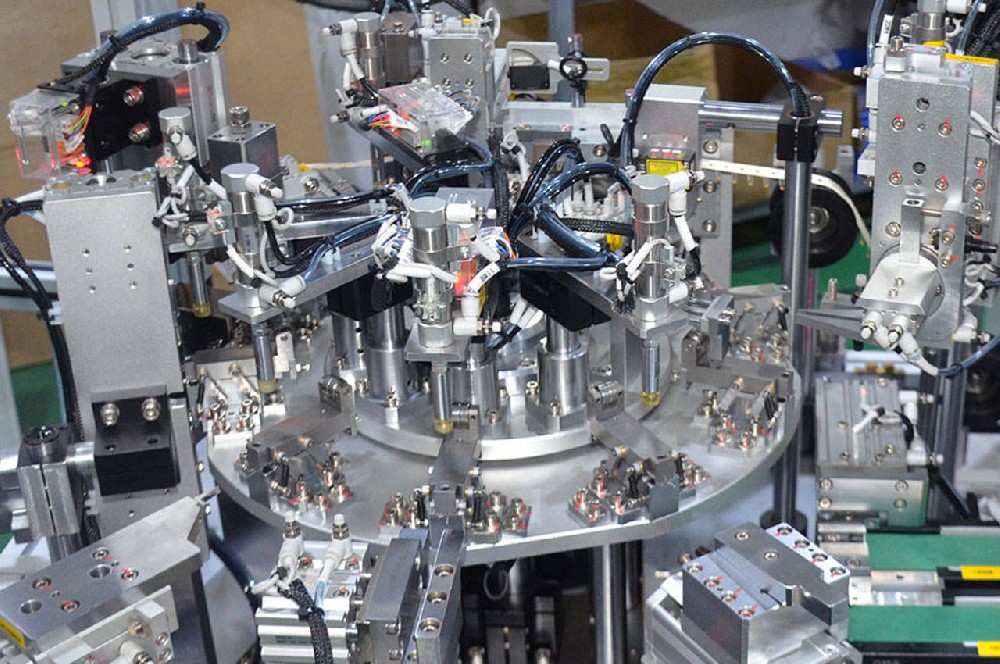
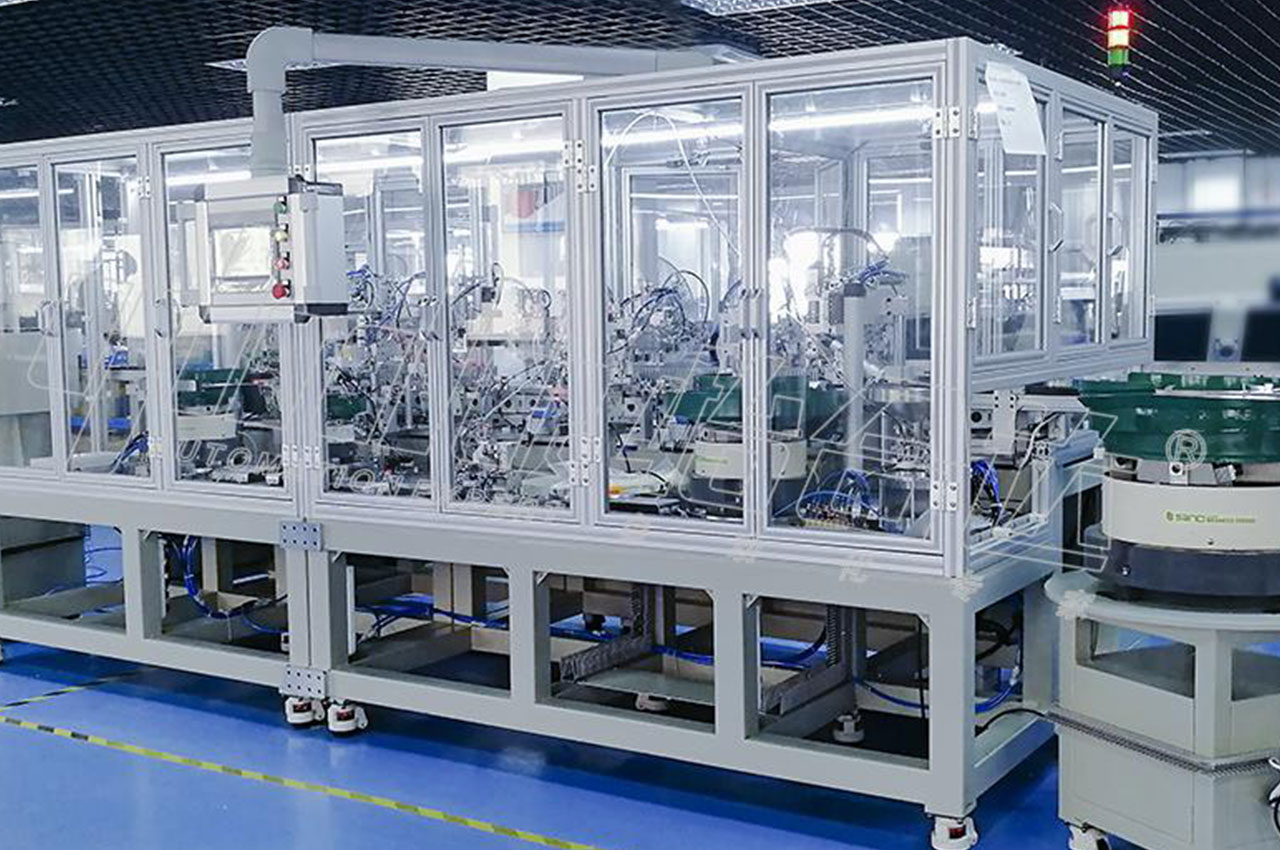
┊ Design planning: According to the characteristics and requirements of the product, the design of automatic assembly system.
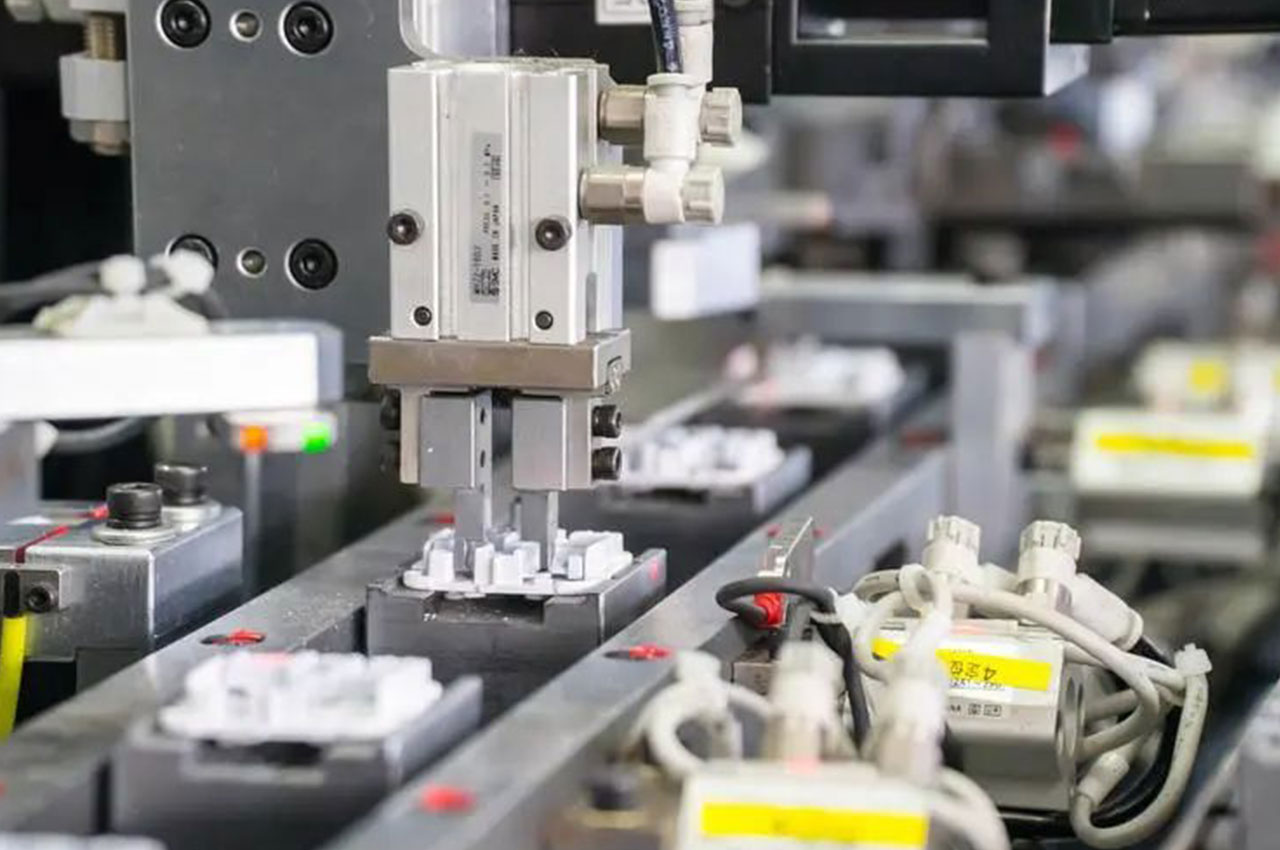
┊ Positioning and grasping: The use of vision systems, sensors and other equipment positioning, through the robotic arm to accurately grasp and place the parts to the assembly position.
┊ Assembly operation: Use a variety of automated assembly tools to perform assembly operations according to predetermined process requirements.
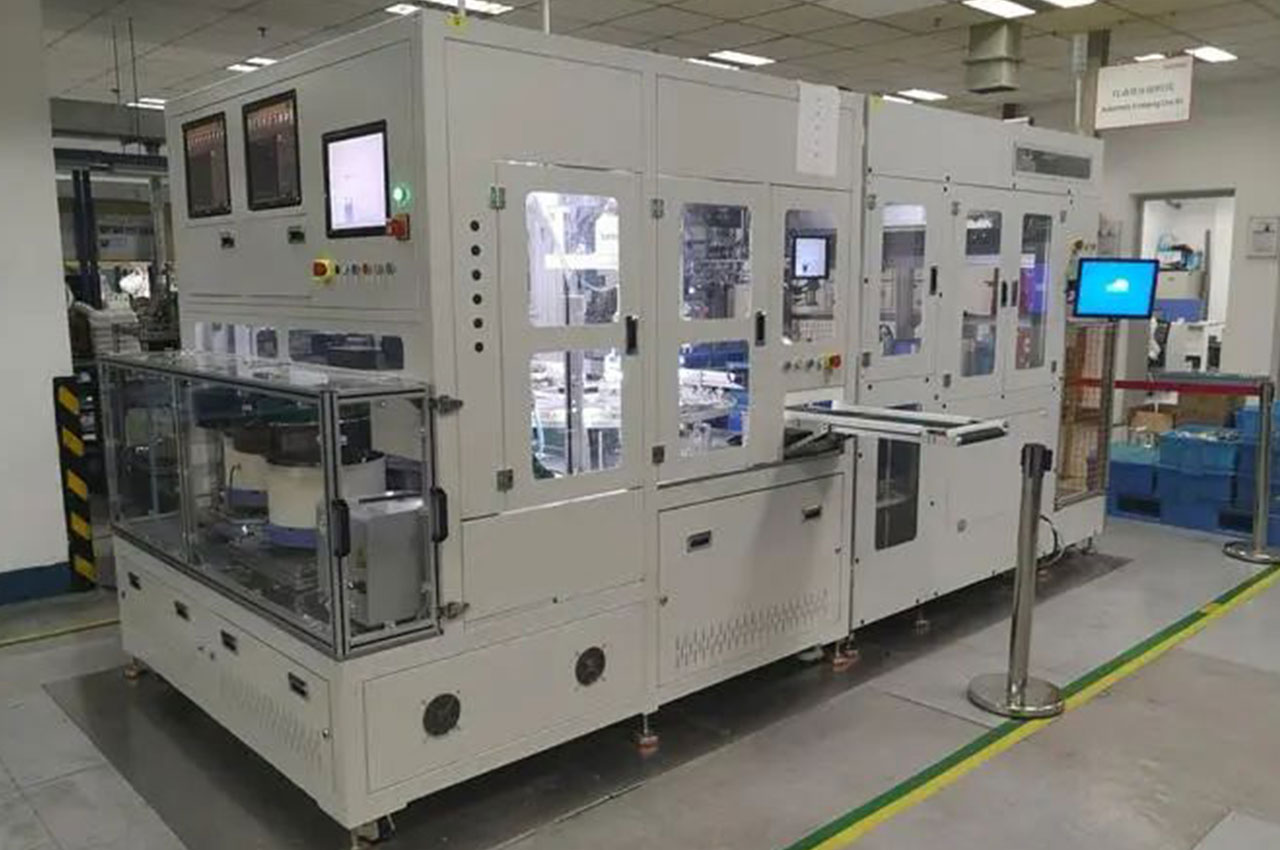
┊ Detection and monitoring: In the assembly process, the assembly quality is tested in real time through various sensors and testing instruments, such as size measurement, torque detection, pressure detection, etc.
┊ Finished product output: The assembled and inspected product is exported to the next step, such as packaging or storage area, through an automated delivery system.
┊ High precision and consistency: A highly accurate and consistent assembly operation is possible thanks to sophisticated machinery and control systems.
┊ High production efficiency: continuous assembly operations can be carried out at a very fast speed, greatly shortening the production cycle and increasing the output.
┊ Low manual intervention: Reduce the dependence on a large number of labor, reduce the error and uncertainty caused by manual operation.
┊ Data monitoring: Collect and analyze production data in real time through sensors and monitoring systems to optimize processes and perform predictive maintenance.
┊ Adapt to large-scale production: can give full play to its scale advantages, reduce unit costs.
┊ High precision requirements for parts: In order to ensure the smooth progress of automated assembly, the accuracy of the size and shape of the parts must strictly meet the design requirements.