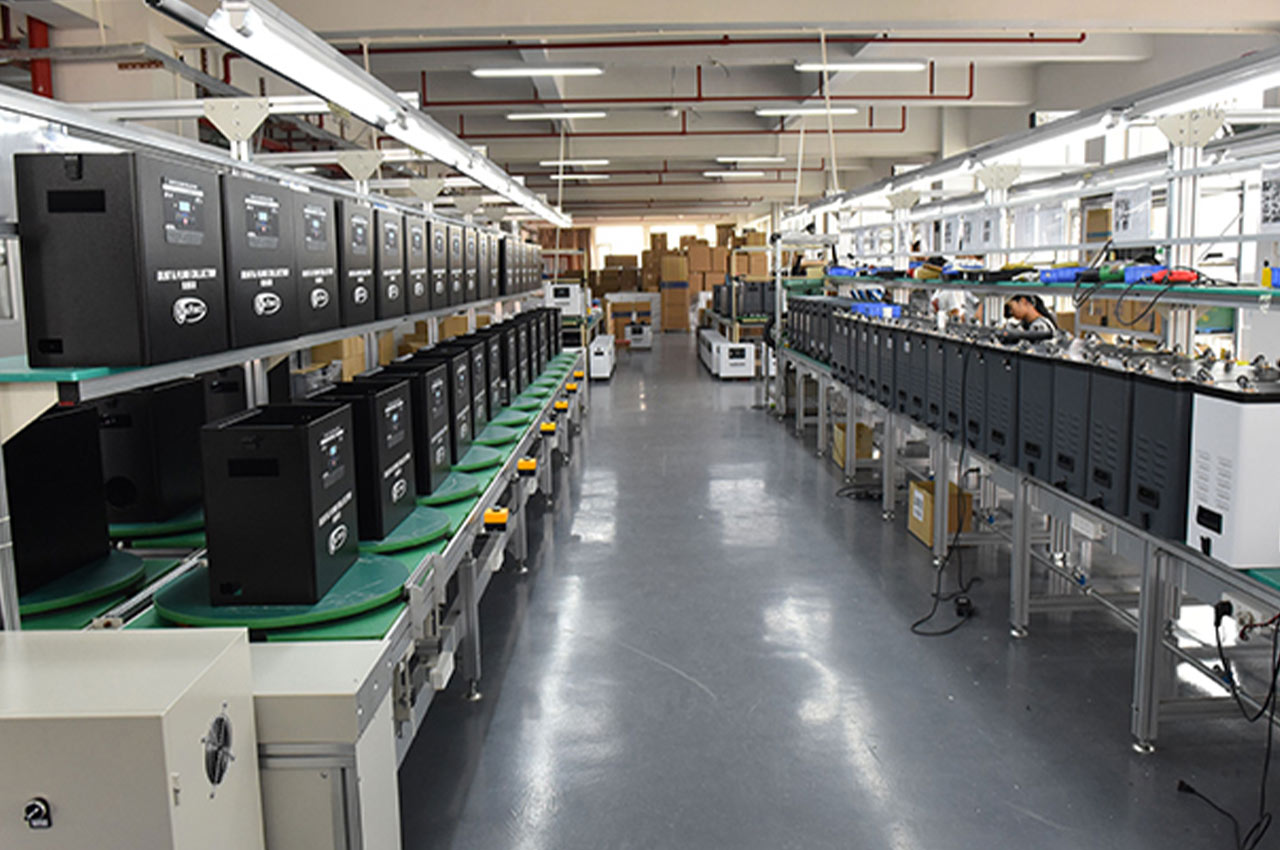
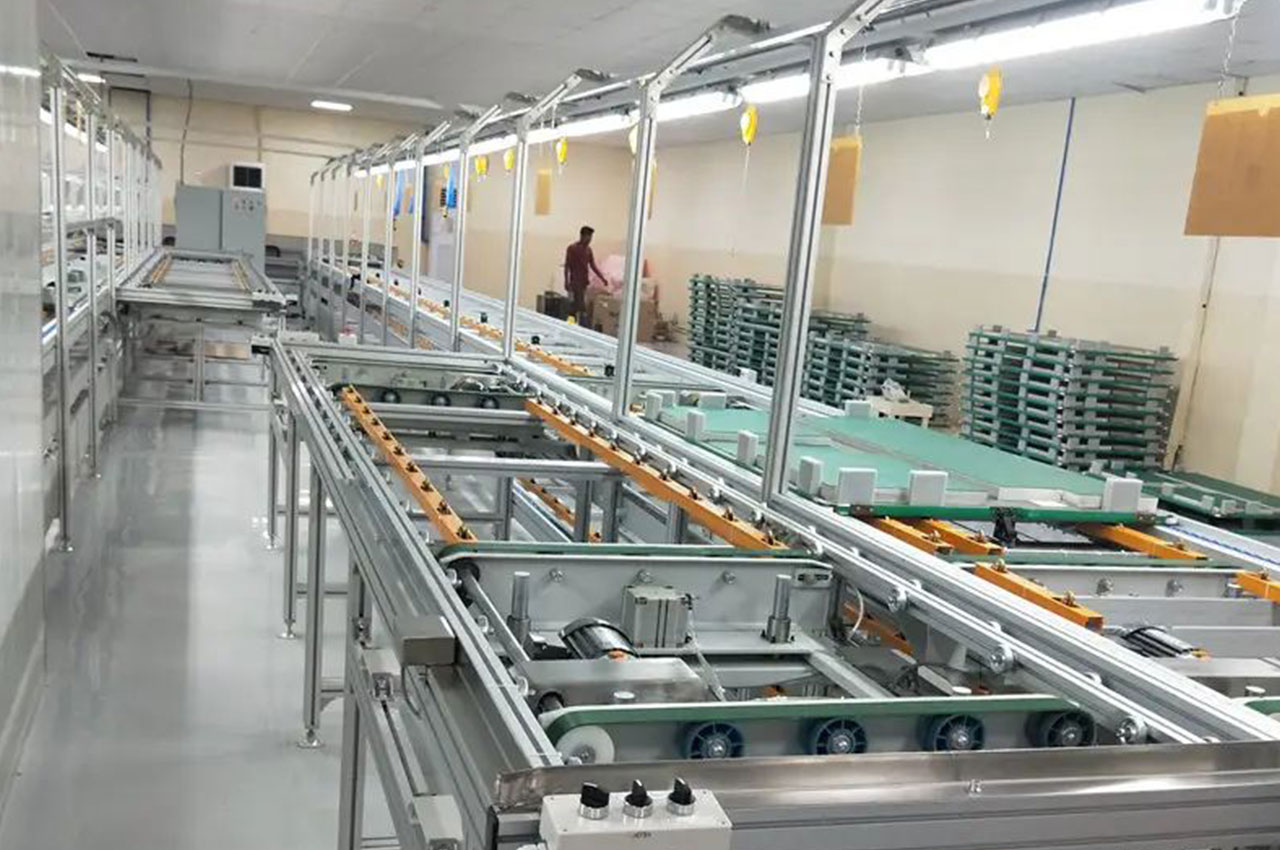
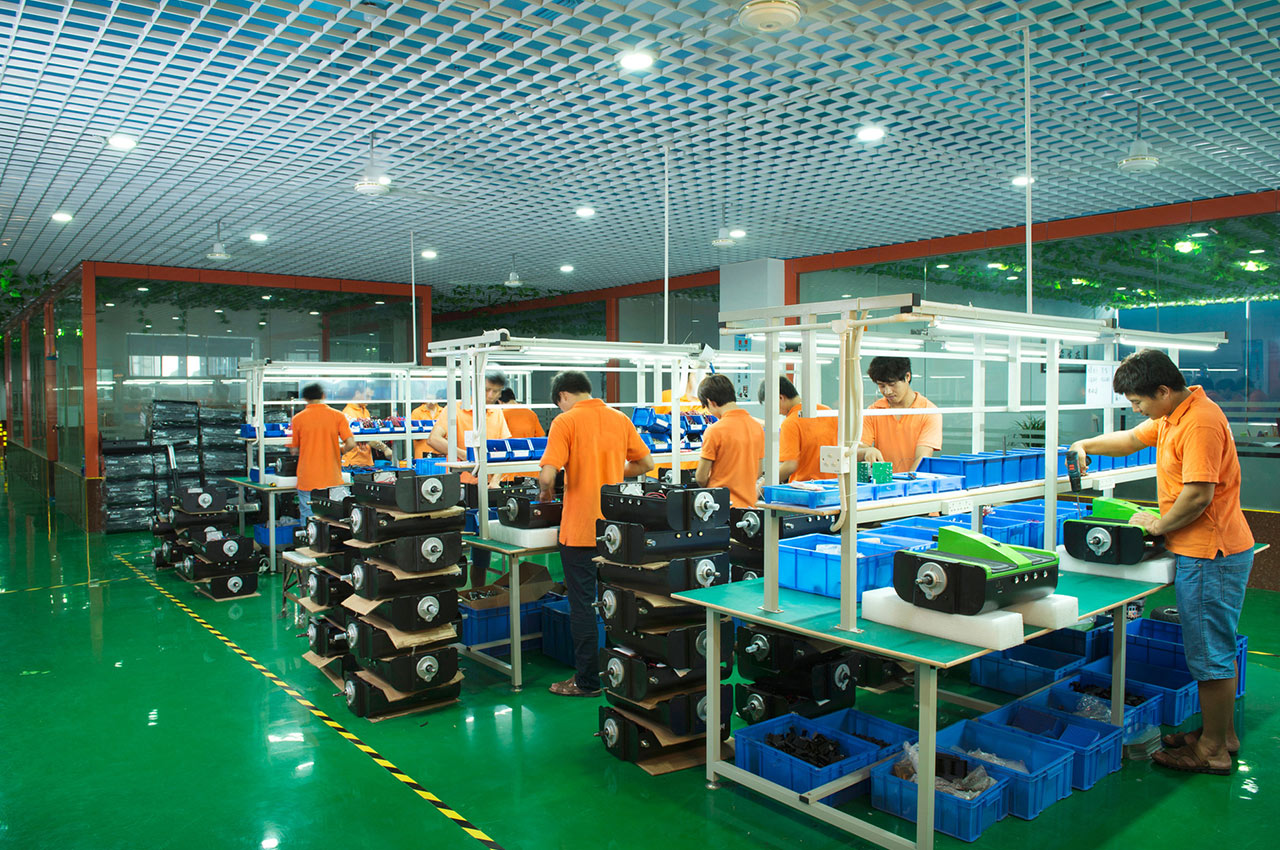
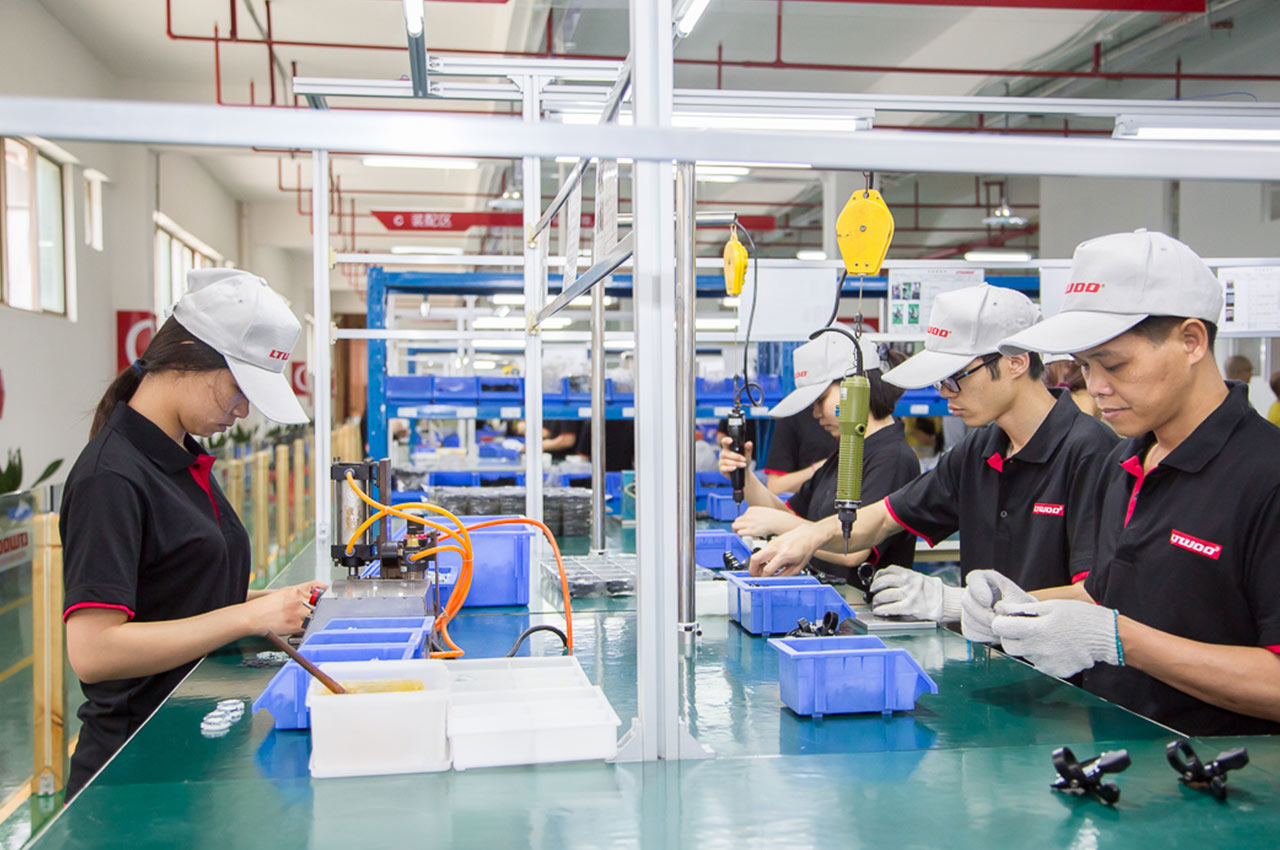
It is the process of combining various parts into a complete product according to the design requirements and process flow.
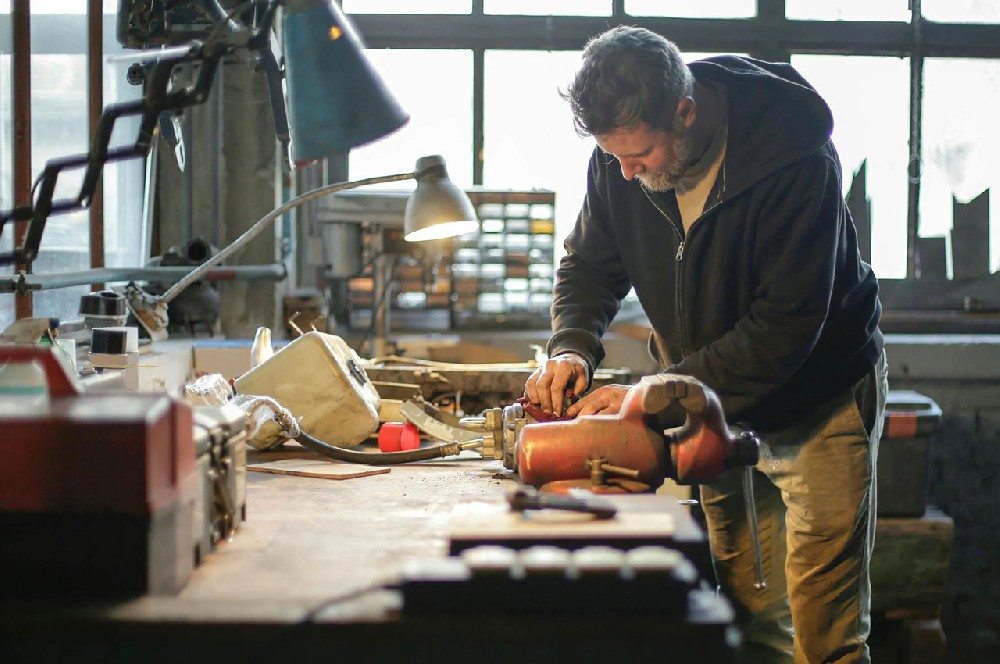

┊ Parts preparation: Procurement, inspection and classification of the required parts to ensure that their quality and specifications meet the requirements.
┊ Preassembly: Some complex components may be assembled in rows to form relatively simple components.
┊ Adjustment and calibration: The adjustment of the assembled parts to ensure that their performance and function meet the requirements.
┊ Testing and inspection: Perform functional testing, appearance inspection, dimensional measurement, etc., to verify the conformity of assembled products.
┊ Cleaning and protection: Remove impurities and oil stains generated during the assembly process, and carry out necessary protective treatment of the product.
┊ Packaging and marking: packaging and marking of qualified products, indicating product model, batch and other information.
┊ Standardized processes: proven operating procedures and specifications to ensure product consistency and quality stability.
┊ Clear division of labor: The division of labor of various assembly links and tasks is clear, and workers focus on specific operations to improve efficiency.
┊ Reliance on manual operation: Although assisted by automated equipment, it still requires manual fine-tuning and assembly.
┊ Parts accuracy requirements are moderate: on the premise of ensuring the overall product performance, the accuracy requirements for parts are relatively not particularly harsh.
┊ Lower cost: Compared to highly automated advanced assembly processes, the input cost of equipment and technology for conventional assembly is usually lower.
┊ Quality inspection process: Through multiple stages of quality inspection, timely discovery and correction of defects and problems.




