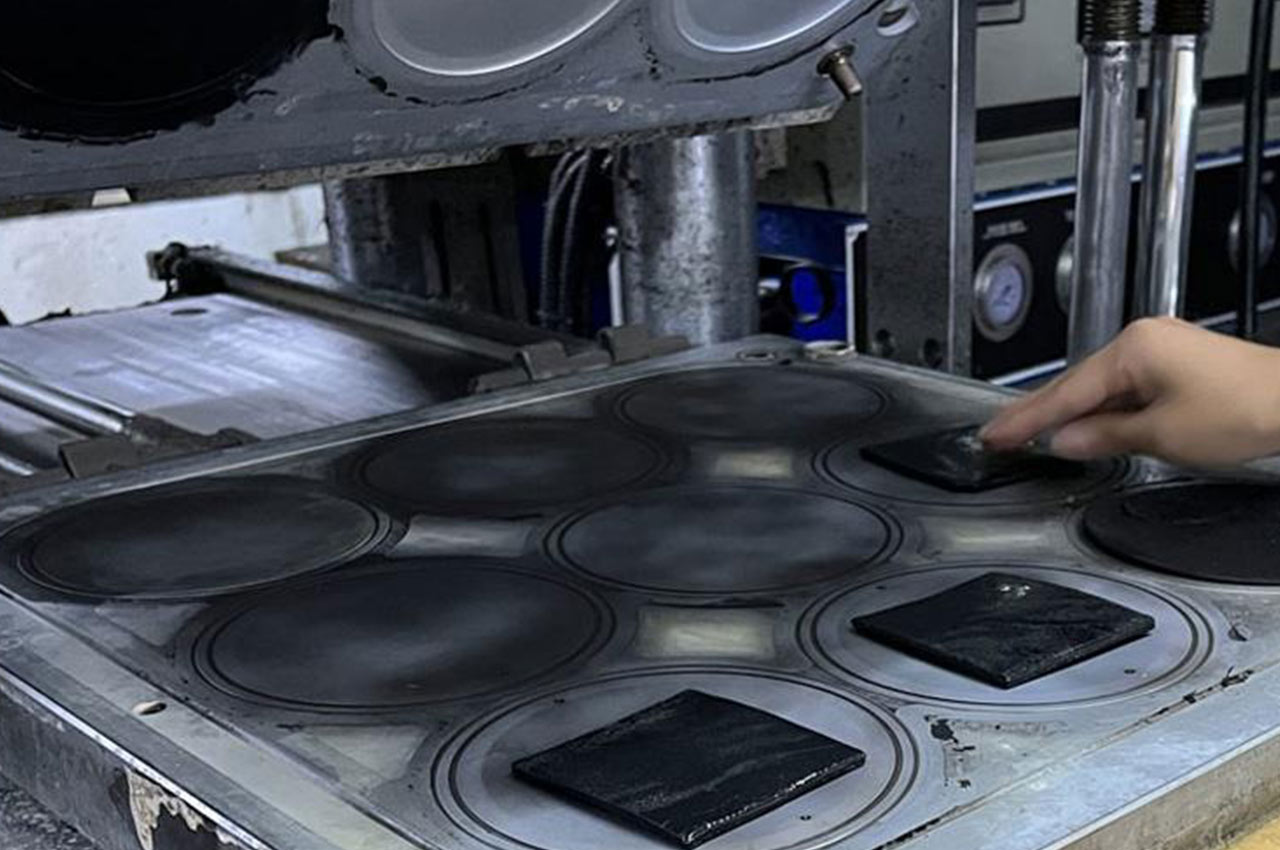
Molding is a process for forming plastic or composite materials. It is to put powder, granular or fibrous plastic or composite materials into the heated mold cavity, and then close the mold pressure, so that it is softened in the mold, melting, and full of mold cavity under pressure, after a certain time of pressure holding and curing, the product with a specific shape and size is obtained after release.
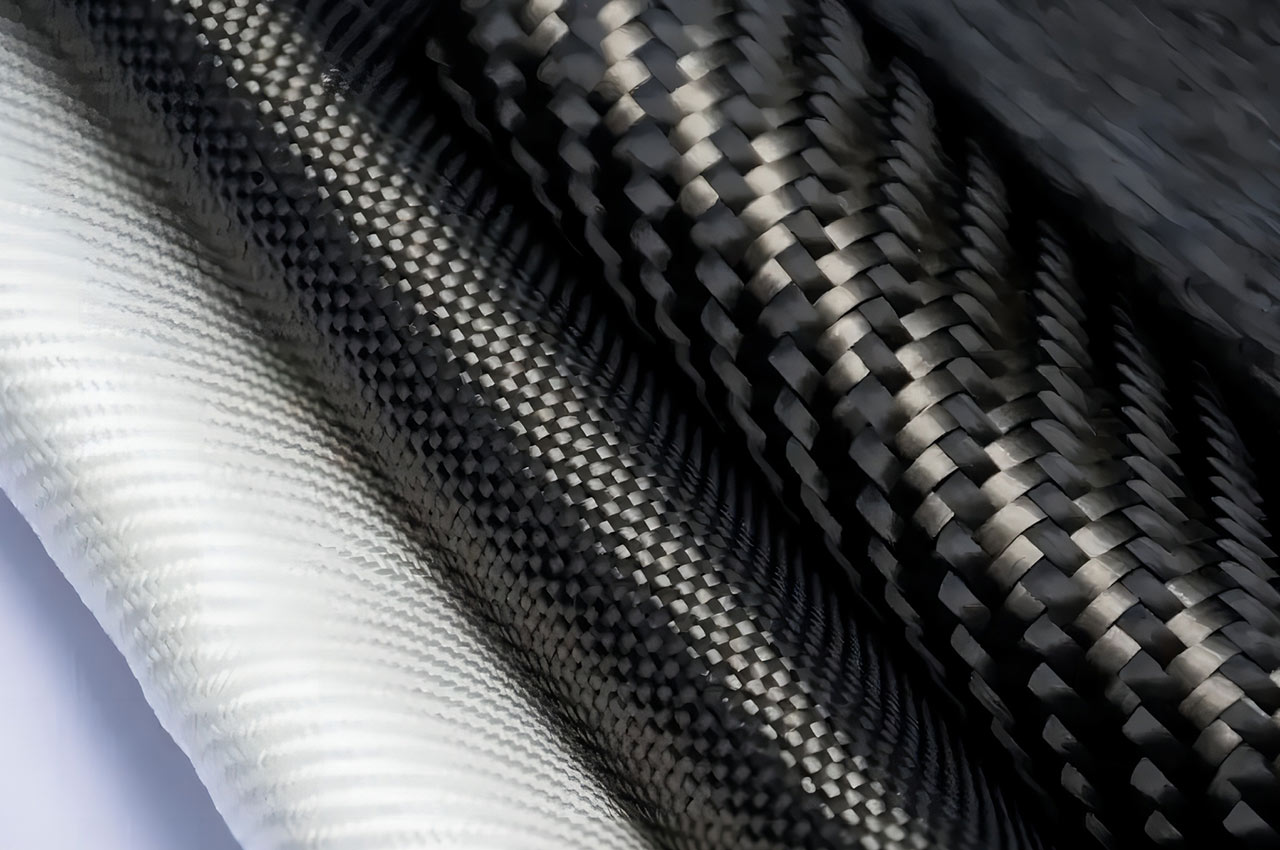

Such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, aramid fiber and resin composite, used to improve the strength and stiffness of products.

┊ Feeding: the premixed material is evenly added to the preheated mold cavity.
┊ Closed mold: Close the mold so that the material is completely enclosed in the mold cavity.
┊ Pressure: Through the hydraulic press or other pressure equipment to apply a certain pressure to the mold, so that the material flows under the pressure, fills the mold cavity, and eliminates the internal gas.
┊ Heating curing: While maintaining the pressure, the mold is heated to make the material cross-linked and solidified. The heating method can be electric heating, steam heating, etc.
┊ Pressure insulation: During the curing process, continue to maintain a certain pressure and temperature for a period of time to ensure that the product is fully cured.
┊ Demoulding: After the product is cured, release the pressure, open the mold, and take out the molded product.
┊ High production efficiency: complex shape products can be formed at one time, reducing subsequent processing processes.
┊ Good dimensional accuracy: Products with high dimensional accuracy can be produced, especially for products with less complex structures.
┊ Excellent product performance: Due to the molding under high temperature and pressure, the product has good mechanical properties, electrical properties and heat resistance.
┊ Mass production: Suitable for large-scale mass production, the cost is relatively low.
┊ High mold cost: The mold design and manufacturing costs of complex products are higher, and the economy of small batch production is not good.
┊ Relatively poor flexibility: once the mold is manufactured, it is difficult to modify the design and size of the product.
┊ Long production cycle: including mold preparation, feeding, curing and other processes, the overall production cycle is relatively long.
